Nervous System
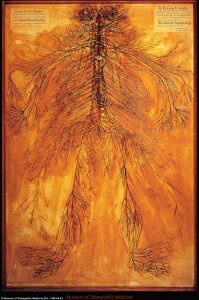
A detailed dissection of the human body’s nervous system
Two components: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
- Central nervous system: brain, spinal cord and nerves
- Peripheral: sensory neurons, ganglia (clusters of neurons) and nerves that connect to one another and the central nervous system to the arms, hands, legs and feet.
Two main subdivisions: the somatic, or voluntary, and the autonomic, or involuntary, component.
- The autonomic nervous system regulates certain body processes, such as blood pressure and the rate of breathing, which work without conscious effort. This system consists of nerves that connect the central nervous system to the lungs, heart, stomach, intestines, bladder, and sex organs.
- The somatic nervous system consists of nerves that connect the brain and spinal cord with muscles and sensory receptors in the skin.
Nerves: cylindrical bundles of fibers that start at the brain and central cord and branch out to every other part of the body.
Neurons send signals to other cells through thin fibers called axons which cause chemicals known as neurotransmitters to be released at junctions called synapses. The synapse gives a command to the cell and the entire communication process typically takes only a fraction of a millisecond.
Sensory neurons react to physical stimuli such as light, sound, and touch, and send feedback to the central nervous system about the body’s surrounding environment. Motor neurons transmit signals to activate muscles or glands. Cranial nervous system: nerves that connect the brain to the eyes, mouth, ears and other parts of the head.
Diseases of the nervous system:
Chronic pain – nerve related
Nerve System disorders cause functional difficulties which result in conditions such as:
- Epilepsy: abnormal electrical discharges from brain cells cause seizures
- Parkinson’s disease: progressive nerve disease that affects movement
- Multiple sclerosis: the protective lining of the nerves is attacked by the body’s immune system
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: motor neuron disease which weakens the muscles and progressively hampers physical function
- Huntington’s disease: inherited – causes the nerve cells in the brain to degenerate
- Alzheimer’s: a wide range of disorders that impacts mental functions, particularly memory
Symptoms and their Emotions
- Alzheimer’s disease: Refusal to deal with the world as it is. Hopelessness and helplessness. Anger.
- Epilepsy: Sense of persecution. Rejection of life. A feeling of great struggle. Self-violence.
- Eye: Represents the capacity to see clearly past, present, future.
- Astigmatism: “I” trouble. Fear of really seeing the self.
- Multiple sclerosis: Mental hardness, hard-heartedness, iron will, inflexibility.
- Nerves: Represent communication. Receptive reporters.
- Pain: Guilt. Guilt always seeks punishment.
- Parkinson’s Disease: Fear and an intense desire to control everything and everyone.
Holistic ways to Heal:

